08、RocketMQ源码解析 - 消费ACK机制之消息进度
1、消息消费进度概述
首先简要阐述一下消息消费进度:
消费者订阅消息消费队列(MessageQueue), 当生产者将消息负载发送到 MessageQueue 中时,消费订阅者开始消费消息,消息消费过程中,为了避免重复消费,需要一个地方存储消费进度(消费偏移量)。
消息模式主要分为集群模式、广播模式:
- 集群模式:一条消息被集群中任何一个消费者消费。
- 广播模式:每条消息都被每一个消费者消费。
广播模式,既然每条消息要被每一个消费者消费,则消费进度可以与消费者保存在一起,也就是本地保存,但由于集群模式下,一条消息只能被集群内的一个消费者消费,进度不能保存在消费端,只能集中保存在一个地方,比较合适的是在 Broker 端。
2、消息消费进度存储接口
接下来我们先分析一下消息消费进度接口:OffsetStore。
/**
* Offset store interface
*/
public interface OffsetStore {
/**
* Load
*
* @throws MQClientException
*/
void load() throws MQClientException;
/**
* Update the offset,store it in memory
*
* @param mq
* @param offset
* @param increaseOnly
*/
void updateOffset(final MessageQueue mq, final long offset, final boolean increaseOnly);
/**
* Get offset from local storage
*
* @param mq
* @param type
* @return The fetched offset
*/
long readOffset(final MessageQueue mq, final ReadOffsetType type);
/**
* Persist all offsets,may be in local storage or remote name server
*
* @param mqs
*/
void persistAll(final Set<MessageQueue> mqs);
/**
* Persist the offset,may be in local storage or remote name server
*
* @param mq
*/
void persist(final MessageQueue mq);
/**
* Remove offset
*
* @param mq
*/
void removeOffset(MessageQueue mq);
/**
* @param topic
* @return The cloned offset table of given topic
*/
Map<MessageQueue, Long> cloneOffsetTable(String topic);
/**
* @param mq
* @param offset
* @param isOneway
*/
void updateConsumeOffsetToBroker(MessageQueue mq, long offset, boolean isOneway) throws RemotingException,
MQBrokerException, InterruptedException, MQClientException;
}
入口代码:DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start()。
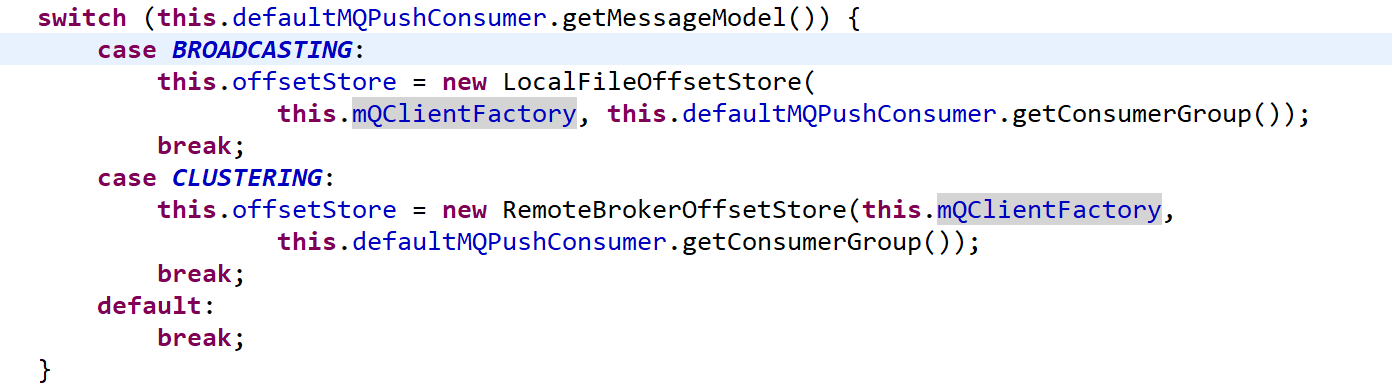
根据消息消费模式(集群模式、广播模式)会创建不同的 OffsetStore 对象。
由于上篇文章,谈到广播模式消息,如果返回 CONSUME_LATER,竟然不会重试,而是直接丢弃,为什么呢?由于这个原因,这次破天荒的从广播模式的OffsetStore开始学习。
2.1 LocalFileOffsetStore (广播模式)
消息进度以本地文件方式保存。源码路径:org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.store.LocalFileOffsetStore。
2.1.1 核心属性与构造函数
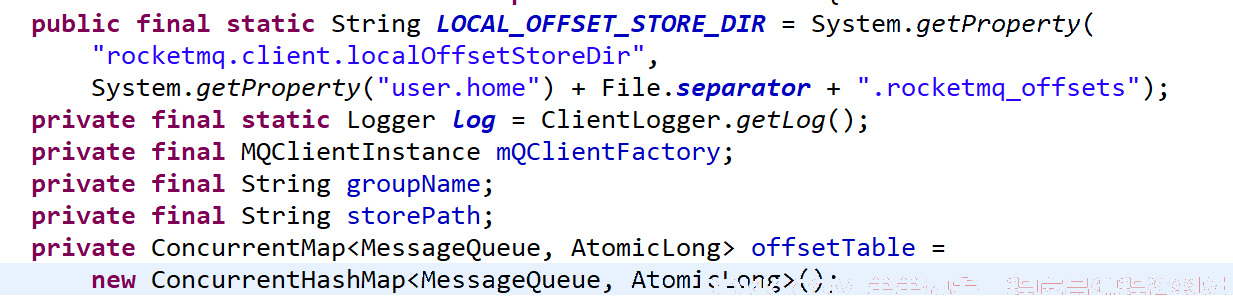
- LOCAL_OFFSET_STORE_DIR
offset 存储根目录,默认为用户主目录,例如 /home/dingw,可以在消费者启动的JVM参数中,通过 - Drocketmq.client.localOffsetStoreDir=路径。 - groupName
消费组名称。 - storePath
具体的消费进度保存文件名(全路径)。 - offsetTable
内存中的 offfset 进度保持,以 MessageQueue 为键,偏移量为值。
继续看一下构造函数:
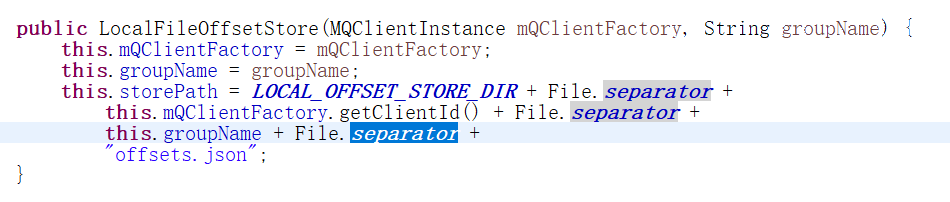
LocalFileOffsetStore 首先在 DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start 方法中创建,并 执行load方法加载消费进度。接下来结束一下几个关键的实现方法。
2.1.2 load()方法
public void load() throws MQClientException {
OffsetSerializeWrapper offsetSerializeWrapper = this.readLocalOffset();
if (offsetSerializeWrapper != null && offsetSerializeWrapper.getOffsetTable() != null) {
offsetTable.putAll(offsetSerializeWrapper.getOffsetTable());
for (MessageQueue mq : offsetSerializeWrapper.getOffsetTable().keySet()) {
AtomicLong offset = offsetSerializeWrapper.getOffsetTable().get(mq);
log.info("load consumer's offset, {} {} {}",
this.groupName,
mq,
offset.get());
}
}
}
该方法,主要就是读取 offsets.json 或 offsets.json.bak 中的内容,然后将json转换成map。

然后更新或获取消息队列的消费进度,就是从内存(Map)或 store 中获取,接下来看一下初次保存offsets.json文件。
@Override
public void persistAll(Set<MessageQueue> mqs) {
if (null == mqs || mqs.isEmpty())
return;
OffsetSerializeWrapper offsetSerializeWrapper = new OffsetSerializeWrapper();
for (Map.Entry<MessageQueue, AtomicLong> entry : this.offsetTable.entrySet()) {
if (mqs.contains(entry.getKey())) {
AtomicLong offset = entry.getValue();
offsetSerializeWrapper.getOffsetTable().put(entry.getKey(), offset);
}
}
String jsonString = offsetSerializeWrapper.toJson(true);
if (jsonString != null) {
try {
MixAll.string2File(jsonString, this.storePath);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("persistAll consumer offset Exception, " + this.storePath, e);
}
}
}
保存逻辑很简单,就没必要一一分析,重点看一下,该方法的调用入口:
MQClientInstance#startScheduledTask
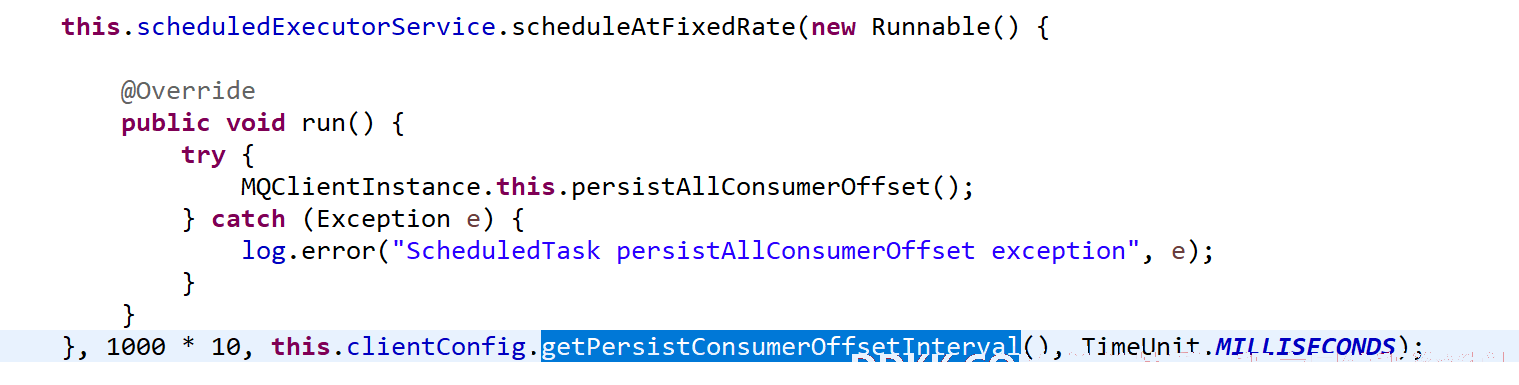
保存逻辑很简单,就没必要一一分析,其调用入口为:MQClientInstance#startScheduledTask。
顺藤摸瓜,原来是一个定时任务,默认消费端启动10秒后,每隔5s的频率持久化一次。
广播模式消费进度存储容易,但其实还是不明白为什么RocketMQ广播模式,如果消费失败,则丢弃,因为广播模式有时候也必须确保每个消费者都成功消费,,通常的场景为,通过MQ刷新本地缓存等。
2.2集群模式消费进度存储(RemoteBrokerOffsetStore)
在阅读RemoteBrokerOffsetStore 之前,我们先思考一下如下的问题:
在集群模式下,多个消费者会负载到不同的消费队列上,因为消息消费进度是基于消息队列进行保存的,也就是不同的消费者之间的消费进度保存是不会存在并发的,但是在同一个消费者,非顺序消息消费时,一个消费者(多个线程)并发消费消息,比如m1 < m2,,但m2先消费完,此时是如何保存的消费进度呢?举个例子,如果m2的offset为5,而m1的offset为4,如果m2先消费完,保存进度为5,那m1消息消费完,保存进度为4,这样岂不乱来了,该如何处理呢?
2.2.1 RemoteBrokerOffsetStore 核心属性
private final static Logger log = ClientLogger.getLog();
// MQ客户端实例,该实例被同一个客户端的消费者、生产者共用
private final MQClientInstance mQClientFactory;
// MQ消费组
private final String groupName;
// 消费进度存储(内存中)
private ConcurrentMap<MessageQueue, AtomicLong> offsetTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<MessageQueue, AtomicLong>();
// 构造方法
public RemoteBrokerOffsetStore(MQClientInstance mQClientFactory, String groupName) {
this.mQClientFactory = mQClientFactory;
this.groupName = groupName;
}
有了广播模式,本地消息消费进度保存等基本认识之后,我们重点来关注 RemoteBrokerOffsetStore 核心方法。
2.2.2 updateOffset
@Override
public void updateOffset(MessageQueue mq, long offset, boolean increaseOnly) {
if (mq != null) {
AtomicLong offsetOld = this.offsetTable.get(mq);
if (null == offsetOld) { // @1
offsetOld = this.offsetTable.putIfAbsent(mq, new AtomicLong(offset)); // @2
}
if (null != offsetOld) { // @3
if (increaseOnly) {
MixAll.compareAndIncreaseOnly(offsetOld, offset); // @4
} else {
offsetOld.set(offset); // @5
}
}
}
}
代码@1:如果当前并没有存储该mq的offset,则把传入的offset放入内存中(map)。
代码@3:如果offsetOld不为空,这里如果不为空,说明同时对一个MQ消费队列进行消费,并发执行。
代码@4,@5:根据 increaseOnly 更新原先的 offsetOld 的值。
2.2.3 readOffset
根据读取来源,读取消费队列的消费进度。
public long readOffset(final MessageQueue mq, final ReadOffsetType type) {
if (mq != null) {
switch (type) {
case MEMORY_FIRST_THEN_STORE: // 先从内存中读取,如果内存中不存在,再尝试从磁盘中读取
case READ_FROM_MEMORY: { // 从内存中读取
AtomicLong offset = this.offsetTable.get(mq);
if (offset != null) {
return offset.get();
} else if (ReadOffsetType.READ_FROM_MEMORY == type) {
return -1;
}
}
case READ_FROM_STORE: { // 从磁盘中读取
try {
long brokerOffset = this.fetchConsumeOffsetFromBroker(mq);
AtomicLong offset = new AtomicLong(brokerOffset);
this.updateOffset(mq, offset.get(), false);
return brokerOffset;
}
// No offset in broker
catch (MQBrokerException e) {
return -1;
}
//Other exceptions
catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("fetchConsumeOffsetFromBroker exception, " + mq, e);
return -2;
}
}
default:
break;
}
}
return -1;
}
这里主要关注从磁盘中读取消费进度,核心入口方法:fetchConsumeOffsetFromBroker。
private long fetchConsumeOffsetFromBroker(MessageQueue mq) throws RemotingException, MQBrokerException,
InterruptedException, MQClientException {
FindBrokerResult findBrokerResult = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInAdmin(mq.getBrokerName());
if (null == findBrokerResult) {
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(mq.getTopic());
findBrokerResult = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInAdmin(mq.getBrokerName());
}
if (findBrokerResult != null) {
QueryConsumerOffsetRequestHeader requestHeader = new QueryConsumerOffsetRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setTopic(mq.getTopic());
requestHeader.setConsumerGroup(this.groupName);
requestHeader.setQueueId(mq.getQueueId());
return this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().queryConsumerOffset(
findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr(), requestHeader, 1000 * 5);
} else {
throw new MQClientException("The broker[" + mq.getBrokerName() + "] not exist", null);
}
}
这里,主要是首先根据 mq 的 broker 名称获取 broker 地址,然后发送请求,我们重点关注一下消费进度是保存在 broker 哪个地方:Broker端的offset管理参照 ConsumerOffsetManager,保存逻辑其实与广播模式差不多,就不深入研究了,重点说一下offset保存的路径:/rocketmq_home/store/config/consumerOffset.json。
综上所述,我们了解到的情况是,广播模式,存放在消费者本地,集群模式,存储在Broker,存储文件,存放的是JSON。
也就是OffsetStore 提供保存消费进度方法,也就是 {“consumeGroup" : [ {”ConsumeQueue1“:offset} ] }。
2.2.4 问题答疑
现在我们思考如下问题:下面讨论还是基于非顺序消息:
1、 集群模式,一个消费组是多个线程消费该队列中的消息,并发执行,例如在q1中存在m1,m2,m3,m4,m5;
最后消费成功的顺序有可能是 m1,m3,m2,m5,m4,如果消费消息,就将该消息的offset存入offset中,岂不是会乱,如果一批拉取了多条消息,消费进度是如何保存的。要解决上述问题,我们移步到到调用offsetStore.updateStore方法,重点看一下那块逻辑:
ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService#processConsumeResult

也就是消息处理后,然后移除该批处理消息,然后返回要更新的offset。那我们重点看一下removeMessage方法:
public long removeMessage(final List<MessageExt> msgs) {
long result = -1;
final long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().lockInterruptibly();
this.lastConsumeTimestamp = now;
try {
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty()) {
result = this.queueOffsetMax + 1;
int removedCnt = 0;
for (MessageExt msg : msgs) {
MessageExt prev = msgTreeMap.remove(msg.getQueueOffset());
if (prev != null) {
removedCnt--;
}
}
msgCount.addAndGet(removedCnt);
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty()) {
result = msgTreeMap.firstKey();
}
}
} finally {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().unlock();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("removeMessage exception", t);
}
return result;
}
主要一下,msgTreeMap 的类型,TreeMap, 按消息的 offset 升序排序,返回的 result, 如果 treemap 中不存在任何消息,那就返回该处理队列最大的偏移量+1,如果移除自己本批消息后,处理队列中,还存在消息,则返回该处理队列中最小的偏移量,也就是此时返回的偏移量有可能不是消息本身的偏移量,而是处理队列中最小的偏移量。
优点:防止消息丢失(也就是没有消费到)。
缺点:会造成消息重复消费。