20、Spring Security 实战 - 会话管理之会话并发控制
前言
现在我们已经掌握了如何防御会话固定攻击,以及在会话过期时的处理策略,但是这些都是针对单个HttpSession来说的,对于会话来说,我们还有另一种情况需要考虑:会话并发控制!
那什么是会话并发控制呢?假如我想实现 “在我们的网站中,同一时刻只允许一个用户登录” 这样的效果,该怎么做?
请各位带着以上的这些问题,跟着 继续往下学习吧。
一. 会话并发控制
1. 会话并发控制
首先我们来了解一下会话并发控制的概念。
有时候出于安全的目的,我们可能会有这样的需求,就是规定在同一个系统中,只允许一个用户在一个终端上登录,这其实就是对会话的并发控制。
2. 并发控制实现思路
如果我们要想上述目标,即同一个用户不能同时在两台设备上登录,我们有两种解决思路:
1、后来的登录自动踢掉前面的登录,例如QQ。
2、如果用户已经登录,则不允许后来者登录。
以上两种思路都能实现这个功能,具体使用哪一个,还要看我们具体的需求。在 Spring Security 框架中,这两种思路都很容易实现,一个配置就可以搞定。
3. 实现方案一:踢掉原有登录用户
我们可以在SecurityConfig配置类中,通过maximumSessions()方法来置单个用户允许同时在线的最大并发会话数,如果没有额外配置,重新登录的会话会踢掉旧的会话。
@EnableWebSecurity(debug = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user/**")
.hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/app/**")
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.csrf()
.disable()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
//进行会话管理
.sessionManagement()
//最大并发会话数,设置单个用户允许同时在线的最大会话数,如果没有额外配置,重新登录的会话会踢掉旧的会话.
.maximumSessions(1);
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
}
maximumSessions: 表示最大并发会话数,设置单个用户允许同时在线的最大会话数,如果没有额外配置,重新登录的会话会踢掉旧的会话。这里配置最大会话数为 1,这样后面的登录就会自动踢掉前面的登录。
配置完成后,分别用 Chrome 和 Firefox 两个浏览器进行测试(或者使用 Chrome 中的多用户功能)。
1、我们先在Firefox 上访问 /user/hello 接口。
2、然后在Chrome 上访问 /user/hello 接口。
等我们在 Firefox 上再次访问 /user/hello 接口时,此时会看到如下提示:
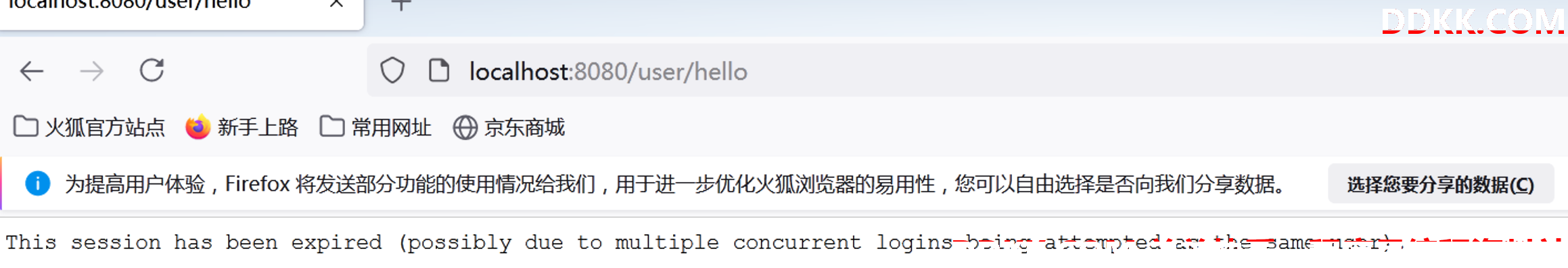
以上信息表明第一个 session 已经过期,原因则是由于使用同一个用户进行并发登录。
4. 实现方案二:阻止新用户登录
如果我们已经有一个用户登录了,这时候这个相同的账号信息还想再次登录,我们可以阻止新用户登录,配置方式如下:
@EnableWebSecurity(debug = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user/**")
.hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/app/**")
.permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.csrf()
.disable()
.formLogin()
.permitAll()
.and()
//进行会话管理
.sessionManagement()
//最大并发会话数,设置单个用户允许同时在线的最大会话数,如果没有额外配置,重新登录的会话会踢掉旧的会话.
.maximumSessions(1)
//当达到最大会话数时,阻止建立新会话,而不是踢掉旧的会话.默认为false
.maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true);
}
/**
* 监听session创建及销毁事件,来及时清理session的记录,以确保最新的session状态可以被及时感知到。
*/
@Bean
public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher() {
return new HttpSessionEventPublisher();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
}
也就是说我们只需要添加 **maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true)**配置即可,此时一个浏览器登录成功后,另外一个浏览器就登录不了了,效果如下:
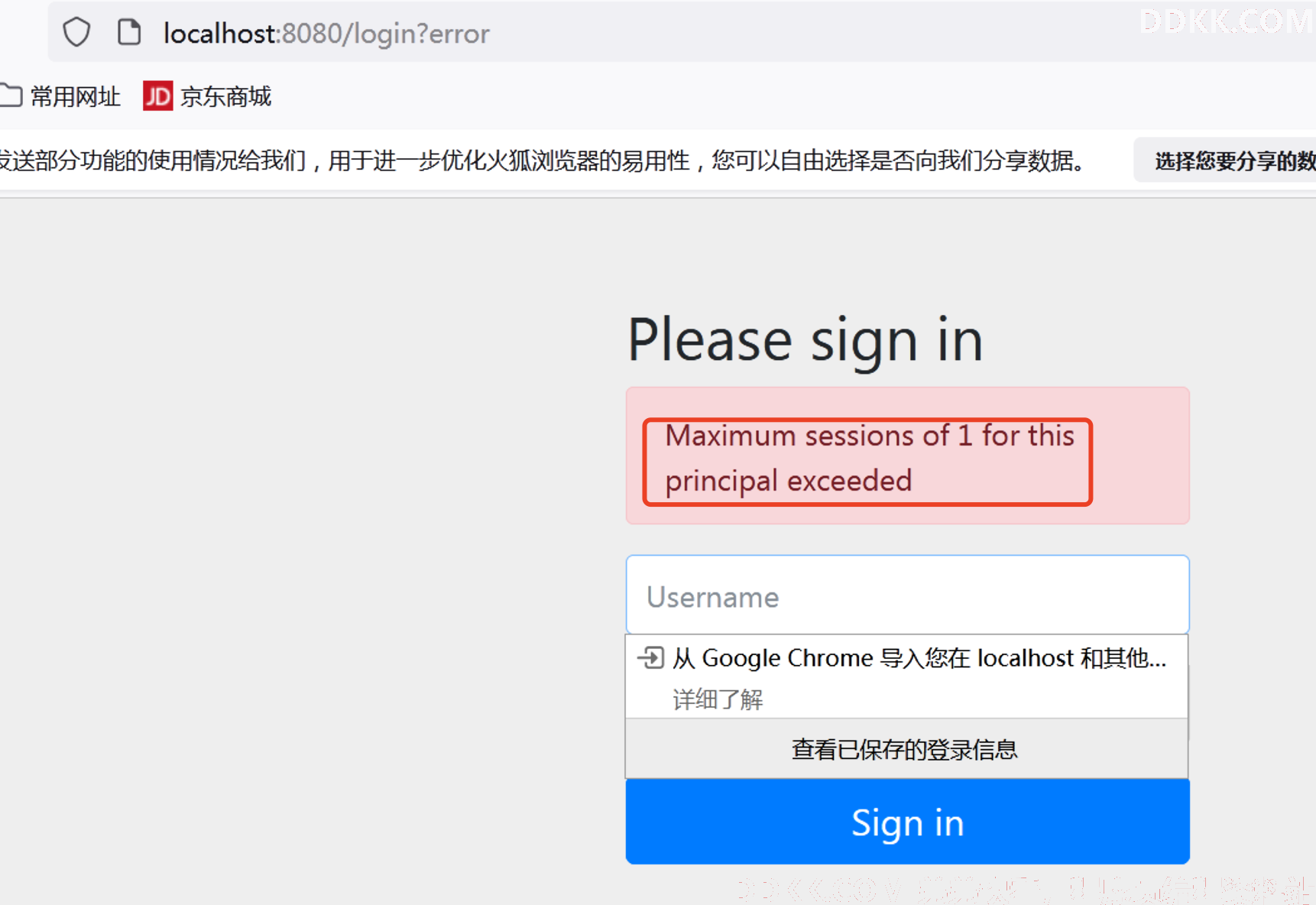
另外我们在上面的源码中,还配置了HttpSessionEventPublisher对象的创建。
注意:
我们之所以要创建HttpSessionEventPublisher这个Bean,是因为在 Spring Security 中,它可以通过监听session的创建及销毁事件,来及时的清理session记录。用户从不同的浏览器登录,都会有对应的session,当用户注销登录之后,session就会失效,但是默认的失效是通过调用 StandardSession#invalidate方法来实现的。这一失效事件无法被 Spring 容器感知到,进而导致当前用户注销登录之后,Spring Security 没有及时清理会话信息表,以为用户还在线,进而导致用户无法重新登录进来。
为了解决这一问题,我们可以提供一个HttpSessionEventPublisher,这个类实现了HttpSessionListener 接口。在该 Bean 中,可以将 session 创建以及销毁的事件及时感知到,并且调用 Spring 中的事件机制将相关的创建和销毁事件发布出去,进而被 Spring Security 感知到,该类部分源码如下:
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent event) {
HttpSessionCreatedEvent e = new HttpSessionCreatedEvent(event.getSession());
Log log = LogFactory.getLog(LOGGER_NAME);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Publishing event: " + e);
}
getContext(event.getSession().getServletContext()).publishEvent(e);
}
/**
* Handles the HttpSessionEvent by publishing a {@link HttpSessionDestroyedEvent} to
* the application appContext.
*
* @param event The HttpSessionEvent pass in by the container
*/
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent event) {
HttpSessionDestroyedEvent e = new HttpSessionDestroyedEvent(event.getSession());
Log log = LogFactory.getLog(LOGGER_NAME);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Publishing event: " + e);
}
getContext(event.getSession().getServletContext()).publishEvent(e);
}
这样我们就实现了会话的并发控制,代码也很简单。
二. 会话并发控制源码解析
两种会话并发控制方案我都已经带着各位实现了,那么底层的实现原理是什么样的呢? 我们一起来看看会话并发控制的源码吧。
1. 会话并发控制执行流程
在Spring Security中,对会话的并发控制也有特定的执行控制流程,该流程是在如下类中被触发执行的:
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter-->AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter-->AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter()
2. AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter()源码
所以我们打开AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter过滤器来看看它的doFilter()方法是怎么定义的。
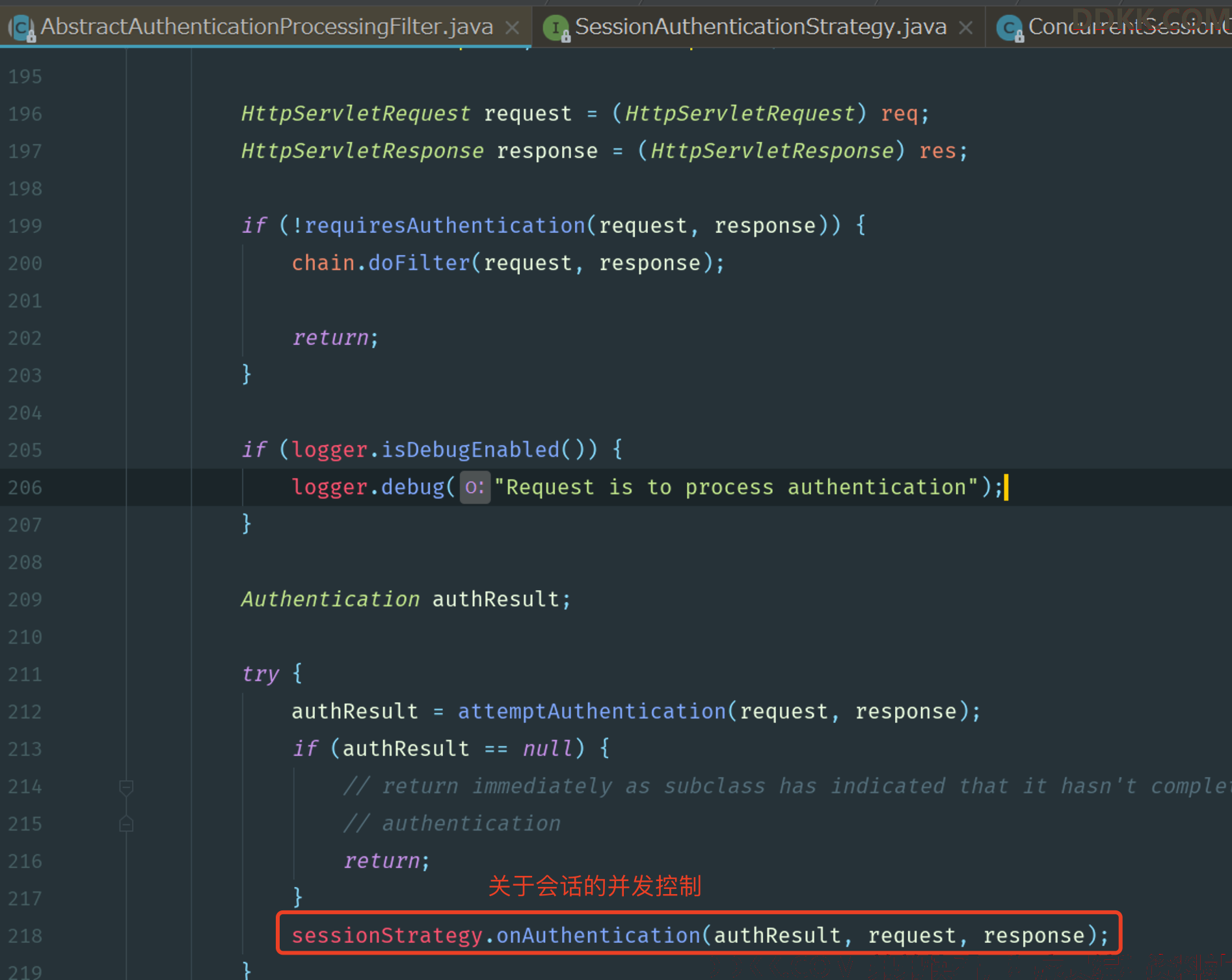
在这段源代码中我们可以看到,在调用完 attemptAuthentication方法执行完认证流程之后,接下来就会调用 sessionStrategy.onAuthentication 方法,这个方法就是用来处理 session 的并发问题的。
3. SessionAuthenticationStrategy接口
接着我们看看sessionStrategy对象所在类SessionAuthenticationStrategy的源码,内部定义了一个onAuthentication()方法*。*
public interface SessionAuthenticationStrategy {
/**
* 当一个新的认证发生时,执行与session相关的功能。
*
*/
void onAuthentication(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws SessionAuthenticationException;
}
我们看看该接口有哪些子类,发现该接口有多个子类,如下图所示:
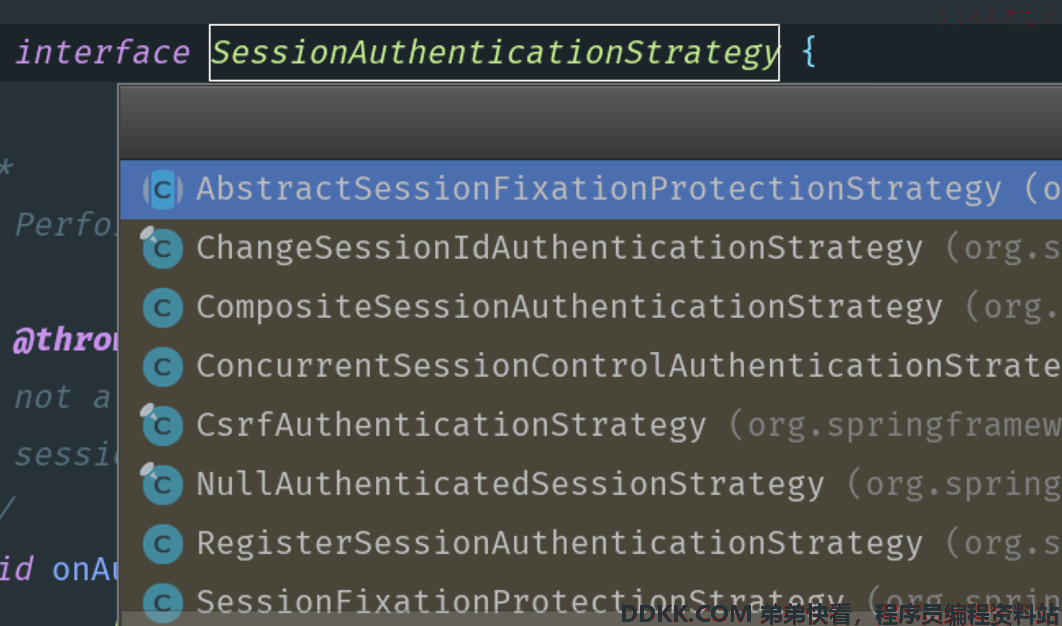
其中默认的实现子类是NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy,如下图所示:
4. ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy
但是当涉及到session的并发处理时,会由ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy这个子类来实现会话并发处理,核心方法如下:
public void onAuthentication(Authentication authentication,
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
final List<SessionInformation> sessions = sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(
authentication.getPrincipal(), false);
int sessionCount = sessions.size();
int allowedSessions = getMaximumSessionsForThisUser(authentication);
if (sessionCount < allowedSessions) {
// They haven't got too many login sessions running at present
return;
}
if (allowedSessions == -1) {
// We permit unlimited logins
return;
}
if (sessionCount == allowedSessions) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
// Only permit it though if this request is associated with one of the
// already registered sessions
for (SessionInformation si : sessions) {
if (si.getSessionId().equals(session.getId())) {
return;
}
}
}
// If the session is null, a new one will be created by the parent class,
// exceeding the allowed number
}
allowableSessionsExceeded(sessions, allowedSessions, sessionRegistry);
}
protected void allowableSessionsExceeded(List<SessionInformation> sessions,
int allowableSessions, SessionRegistry registry)
throws SessionAuthenticationException {
if (exceptionIfMaximumExceeded || (sessions == null)) {
throw new SessionAuthenticationException(messages.getMessage(
"ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy.exceededAllowed",
new Object[] {allowableSessions},
"Maximum sessions of {0} for this principal exceeded"));
}
// Determine least recently used sessions, and mark them for invalidation
sessions.sort(Comparator.comparing(SessionInformation::getLastRequest));
int maximumSessionsExceededBy = sessions.size() - allowableSessions + 1;
List<SessionInformation> sessionsToBeExpired = sessions.subList(0, maximumSessionsExceededBy);
for (SessionInformation session: sessionsToBeExpired) {
session.expireNow();
}
}
这段核心代码主要含义如下:
1、首先调用 sessionRegistry.getAllSessions() 方法获取当前用户的所有 session信息,该方法在调用时会传递两个参数:一个是当前用户的 authentication,另一个参数 false 表示不包含已经过期的 session(在用户登录成功后,会将用户的 sessionid 存起来,其中 key 是用户的主体(principal),value 则是该主题对应的 sessionid 组成的一个集合)。
2、接下来计算当前用户已经有几个有效的 session,同时获取允许的 session 并发数。
3、如果当前 session 数(sessionCount)小于 session 并发数(allowedSessions),则不做任何处理;如果 allowedSessions 的值为 -1,表示对 session 数量不做任何限制。
4、如果当前的 session 数(sessionCount)等于 session 并发数(allowedSessions),那就先看看当前 session对象是否不为null,并且是否已经存在于 sessions 中了。如果已经存在了,则不做任何处理;如果当前 session 为 null,那么意味着将有一个新的 session 被创建出来,届时当前 session 数(sessionCount)就会超过 session 并发数(allowedSessions)。
5、如果前面的代码中都没能 return 掉,那么将进入策略判断方法 allowableSessionsExceeded 中。
6、在allowableSessionsExceeded 方法中,首先会有 exceptionIfMaximumExceeded 属性,这就是我们在 SecurityConfig 中配置的 maxSessionsPreventsLogin 的值,默认为 false。如果为 true,就直接抛出异常,那么这次登录就失败了;如果为 false,则对 sessions 按照请求时间进行排序,然后再使多余的 session 过期即可。
至此, 就跟大家讲解了会话并发控制的两种实现方案,并且给大家讲解了底层的实现源码,请各位照着我的文章进行实现和阅读,有不明白之处,请在评论区留言!