21、Solr4.8.0源码分析(21)之SolrCloud的Recovery策略(二)
题记:前文<Solr4.8.0源码分析(20)之SolrCloud的Recovery策略(一)>中提到Recovery有两种策略,一是PeerSync和Replication。本节将具体介绍下PeerSync策略。
PeeySync是Solr的优先选择策略,每当需要进行recovery了,Solr总是会先去判断是否需要进入PeerSync,只有当PeerSync被设置为跳过或者PeerSync时候发现没符合条件才会进入到Replication。这是由PeeySync的特性决定的,PeeySync是面向中断时间短,需要recovery的document个数较少时使用的策略,因此它Recovery的速度较快,对Solr的影响较小。而Replication则是对中断时间长,需要recovery数量多的情况下进行的,耗时较长。
前文已经介绍了Recovery的总体流程,那么本文就直接来介绍PeerSync的流程了,请看下图所示:
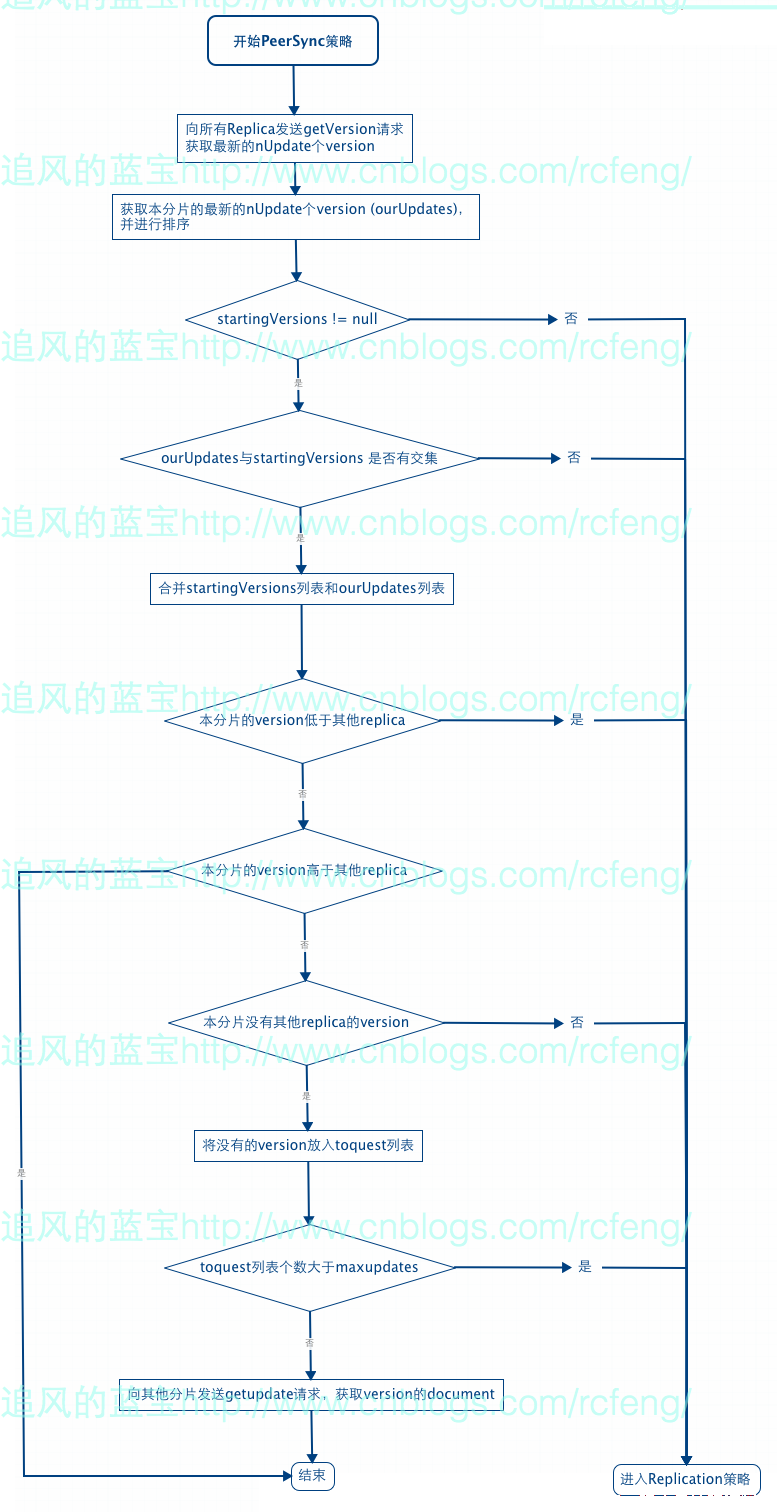
- 首先 Solr会向所有Replica发送getversion的请求,来获取最新的nupdate个version(默认是100个)。
// Fire off the requests before getting our own recent updates (for better concurrency)
// This also allows us to avoid getting updates we don't need... if we got our updates and then got their updates, they would
// have newer stuff that we also had (assuming updates are going on and are being forwarded).
for (String replica : replicas) {
requestVersions(replica);
}
private void requestVersions(String replica) {
SyncShardRequest sreq = new SyncShardRequest();
sreq.purpose = 1;
sreq.shards = new String[]{replica};
sreq.actualShards = sreq.shards;
sreq.params = new ModifiableSolrParams();
sreq.params.set("qt","/get");
sreq.params.set("distrib",false);
sreq.params.set("getVersions",nUpdates);
shardHandler.submit(sreq, replica, sreq.params);
}
- 获取本分片最新的nupdate个version(默认是100个),并对这些version进行排序。
recentUpdates = ulog.getRecentUpdates();
try {
ourUpdates = recentUpdates.getVersions(nUpdates);
} finally {
recentUpdates.close();
}
Collections.sort(ourUpdates, absComparator);
- 获取recovery之前的version信息startingversions。通过比较startingversions与ourUpdates可以来比较recovery期间是否有索引更新。
- 检查ourUpdates和startingversions是否有交集,由于ourUpdates和startingversions的version个数是限制为nUpdates的,也就是判断索引更新的个数是否大于nUpdate。如果需要更新的索引太多即ourUpdates和startingversions无交集,则进入Replication。
// now make sure that the starting updates overlap our updates
// there shouldn't be reorders, so any overlap will do.
long smallestNewUpdate = Math.abs(ourUpdates.get(ourUpdates.size()-1));
if (Math.abs(startingVersions.get(0)) < smallestNewUpdate) {
log.warn(msg() + "too many updates received since start - startingUpdates no longer overlaps with our currentUpdates");
return false;
}
- 如果ourUpdates和startingversions有交集,则合并两个列表,即求并集。
// let's merge the lists
List<Long> newList = new ArrayList<>(ourUpdates);
for (Long ver : startingVersions) {
if (Math.abs(ver) < smallestNewUpdate) {
newList.add(ver);
}
}
ourUpdates = newList;
- 本分片的version比别的分片低,则进入Replication策略。这里进行分片version的比较,并没有按version的最大或者最小值,而是比较0.8和0.2比例处的version。
long otherHigh = percentile(otherVersions, .2f);
long otherLow = percentile(otherVersions, .8f);
if (ourHighThreshold < otherLow) {
// Small overlap between version windows and ours is older
// This means that we might miss updates if we attempted to use this method.
// Since there exists just one replica that is so much newer, we must
// fail the sync.
log.info(msg() + " Our versions are too old. ourHighThreshold="+ourHighThreshold + " otherLowThreshold="+otherLow);
return false;
}
- 如果本分片的version比其他分片高,则说明不需要进行recovery直接退出peersync。
if (ourLowThreshold > otherHigh) {
// Small overlap between windows and ours is newer.
// Using this list to sync would result in requesting/replaying results we don't need
// and possibly bringing deleted docs back to life.
log.info(msg() + " Our versions are newer. ourLowThreshold="+ourLowThreshold + " otherHigh="+otherHigh);
return true;
}
- 对本分片的version和其他分片的version求差,获取本分片缺少的version。
for (Long otherVersion : otherVersions) {
// stop when the entries get old enough that reorders may lead us to see updates we don't need
if (!completeList && Math.abs(otherVersion) < ourLowThreshold) break;
if (ourUpdateSet.contains(otherVersion) || requestedUpdateSet.contains(otherVersion)) {
// we either have this update, or already requested it
// TODO: what if the shard we previously requested this from returns failure (because it goes
// down)
continue;
}
toRequest.add(otherVersion);
requestedUpdateSet.add(otherVersion);
}
最后向其他分片发送getupdate命令,根据处理后的version获取相应的document,至此完成peersync过程
private boolean requestUpdates(ShardResponse srsp, List<Long> toRequest) {
String replica = srsp.getShardRequest().shards[0];
log.info(msg() + "Requesting updates from " + replica + "n=" + toRequest.size() + " versions=" + toRequest);
// reuse our original request object
ShardRequest sreq = srsp.getShardRequest();
sreq.purpose = 0;
sreq.params = new ModifiableSolrParams();
sreq.params.set("qt", "/get");
sreq.params.set("distrib", false);
sreq.params.set("getUpdates", StrUtils.join(toRequest, ','));
sreq.params.set("onlyIfActive", onlyIfActive);
sreq.responses.clear(); // needs to be zeroed for correct correlation to occur
shardHandler.submit(sreq, sreq.shards[0], sreq.params);
return true;
}
总结:
本文具体介绍PeerSync的过程,由此可见PeerSync策略的recovery过程还是比较简单的,下一节将具体介绍Replication策略,这个较PeerSync复杂。