25、Spring源码分析 - 25-Spring异步实现原理
@EnableAsync用于开启Spring bean异步方法的能力。下面是注解EnableAsync的定义。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAsync {
//默认只赋予@Async和@javax.ejb.Asynchronous方法异步的能力,可通过该属性覆盖扩展
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
//异步方法的代理对象是否使用cglib
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
//默认使用JDK动态代理
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
//最低优先级
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
1、注册AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
默认情况下EnableAsync#mode()为AdviceMode.PROXY,AsyncConfigurationSelector的selectImports()方法返回的@Configuartion类ProxyAsyncConfiguration里面注册了一个AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,这个BeanPostProcessor为每个有@Async的类或方法的类生成一个有异步方法调用能力的代理对象。
public class AsyncConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableAsync> {
private static final String ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME =
"org.springframework.scheduling.aspectj.AspectJAsyncConfiguration";
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
//不同模式使用不同代理技术,默认是PROXY JDK动态代理
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {ProxyAsyncConfiguration.class.getName()};
//AspectJ静态织入
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};
default:
return null;
}
}
}
AsyncConfigurationSelector.selectImports()方法是在父类AdviceModeImportSelector的ImportSelector接口方法selectImports()调用时被调用的。
public abstract class AdviceModeImportSelector<A extends Annotation> implements ImportSelector {
public static final String DEFAULT_ADVICE_MODE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME = "mode";
protected String getAdviceModeAttributeName() {
return DEFAULT_ADVICE_MODE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME;
}
@Override
public final String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
//@EnableAsync
Class<?> annType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(getClass(), AdviceModeImportSelector.class);
Assert.state(annType != null, "Unresolvable type argument for AdviceModeImportSelector");
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annType);
if (attributes == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"@%s is not present on importing class '%s' as expected",
annType.getSimpleName(), importingClassMetadata.getClassName()));
}
AdviceMode adviceMode = attributes.getEnum(getAdviceModeAttributeName());
//子类实现
String[] imports = selectImports(adviceMode);
if (imports == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown AdviceMode: " + adviceMode);
}
return imports;
}
@Nullable
protected abstract String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode);
}
ProxyAsyncConfiguration的@Bean方法内,注册了一个AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor并配置了Supplier
@Configuration
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyAsyncConfiguration extends AbstractAsyncConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.ASYNC_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor asyncAdvisor() {
Assert.notNull(this.enableAsync, "@EnableAsync annotation metadata was not injected");
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor bpp = new AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
bpp.configure(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler);
Class<? extends Annotation> customAsyncAnnotation = this.enableAsync.getClass("annotation");
if (customAsyncAnnotation != AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(EnableAsync.class, "annotation")) {
bpp.setAsyncAnnotationType(customAsyncAnnotation);
}
bpp.setProxyTargetClass(this.enableAsync.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass"));
bpp.setOrder(this.enableAsync.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
return bpp;
}
}
@Configuration
public abstract class AbstractAsyncConfiguration implements ImportAware {
@Nullable
protected AnnotationAttributes enableAsync;
@Nullable
protected Supplier<Executor> executor;
@Nullable
protected Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler;
@Override
public void setImportMetadata(AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) {
this.enableAsync = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(
importMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableAsync.class.getName(), false));
if (this.enableAsync == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"@EnableAsync is not present on importing class " + importMetadata.getClassName());
}
}
@Autowired(required = false)
void setConfigurers(Collection<AsyncConfigurer> configurers) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
return;
}
if (configurers.size() > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Only one AsyncConfigurer may exist");
}
AsyncConfigurer configurer = configurers.iterator().next();
this.executor = configurer::getAsyncExecutor;
this.exceptionHandler = configurer::getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
}
}
2、@Async类通知器的构成
目标对象在经过AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法后会返回一个代理对象替换元对象。先看一下AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的继承结构。
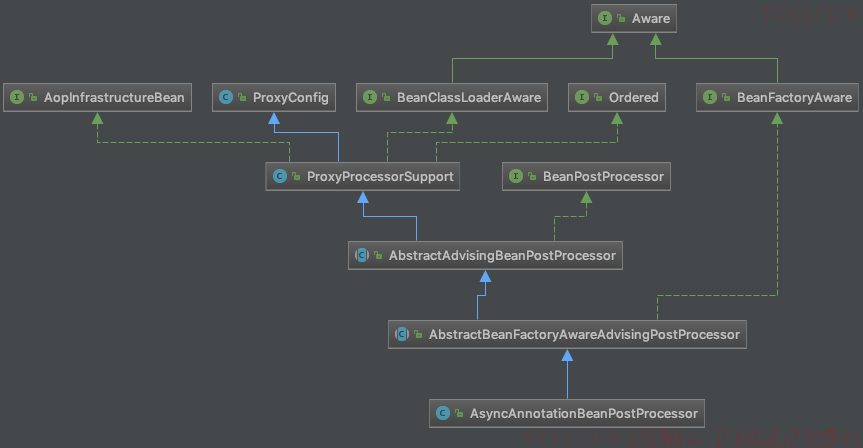
AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor实现了接口BeanFactoryAware的setBeanFactory()方法,而AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor又重写了此方法,此方法的调用要早于接口BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,下面是AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.setBeanFactory()方法。
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
AsyncAnnotationAdvisor advisor = new AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler);
if (this.asyncAnnotationType != null) {
advisor.setAsyncAnnotationType(this.asyncAnnotationType);
}
advisor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.advisor = advisor;
}
这个方法内实例化了一个AsyncAnnotationAdvisor并保存在了父类AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor的成员变量advisor。AsyncAnnotationAdvisor是继承了AbstractPointcutAdvisor实现了getAdvice()和getPointcut()方法。这两个方法的返回值就是上面方法实例化AsyncAnnotationAdvisor就确定的。
public class AsyncAnnotationAdvisor extends AbstractPointcutAdvisor implements BeanFactoryAware {
private Advice advice;
private Pointcut pointcut;
public AsyncAnnotationAdvisor() {
this((Supplier<Executor>) null, (Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler>) null);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(
@Nullable Executor executor, @Nullable AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) {
this(SingletonSupplier.ofNullable(executor), SingletonSupplier.ofNullable(exceptionHandler));
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(
@Nullable Supplier<Executor> executor, @Nullable Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler) {
Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(2);
//@Async和@Asynchronous是默认支持的
asyncAnnotationTypes.add(Async.class);
try {
asyncAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.ejb.Asynchronous", AsyncAnnotationAdvisor.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// If EJB 3.1 API not present, simply ignore.
}
this.advice = buildAdvice(executor, exceptionHandler);
this.pointcut = buildPointcut(asyncAnnotationTypes);
}
//@Async的value 可以覆盖构造器中默认的注解类型
public void setAsyncAnnotationType(Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType) {
Assert.notNull(asyncAnnotationType, "'asyncAnnotationType' must not be null");
Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes = new HashSet<>();
asyncAnnotationTypes.add(asyncAnnotationType);
this.pointcut = buildPointcut(asyncAnnotationTypes);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.advice instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) this.advice).setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}
@Override
public Advice getAdvice() {
return this.advice;
}
@Override
public Pointcut getPointcut() {
return this.pointcut;
}
protected Advice buildAdvice(
@Nullable Supplier<Executor> executor, @Nullable Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler) {
AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor interceptor = new AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor(null);
interceptor.configure(executor, exceptionHandler);
return interceptor;
}
/**
* Calculate a pointcut for the given async annotation types, if any.
* @param asyncAnnotationTypes the async annotation types to introspect
* @return the applicable Pointcut object, or {@code null} if none
*/
protected Pointcut buildPointcut(Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes) {
ComposablePointcut result = null;
for (Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType : asyncAnnotationTypes) {
Pointcut cpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(asyncAnnotationType, true);
Pointcut mpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(null, asyncAnnotationType, true);
if (result == null) {
result = new ComposablePointcut(cpc);
}
else {
result.union(cpc);
}
result = result.union(mpc);
}
return (result != null ? result : Pointcut.TRUE);
}
}
buildAdvice()方法返回的是一个AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor(),并传入AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的executor和exceptionHandler。接下来就看一下这个通知具体行为。继承结构如下:
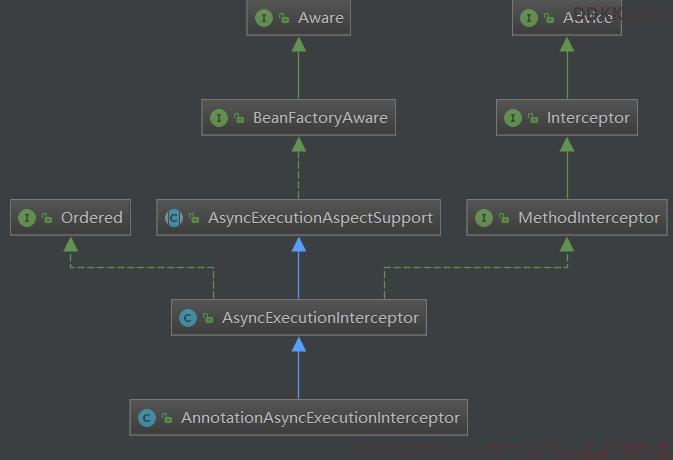
可以看到AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor是MethodInterceptor接口的实现类,下面看一下invoke()方法的实现:
public class AsyncExecutionInterceptor extends AsyncExecutionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Ordered {
public AsyncExecutionInterceptor(@Nullable Executor defaultExecutor) {
//调用父类构造方法,在祖先类AsyncExecutionAspectSupport的同方法签名构造函数中,如果defaultExecutor为null,会创建默认的,如下面注释
//this.defaultExecutor = new SingletonSupplier<>(defaultExecutor, () -> getDefaultExecutor(this.beanFactory));
//this.exceptionHandler = SingletonSupplier.of(SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler::new);
super(defaultExecutor);
}
public AsyncExecutionInterceptor(@Nullable Executor defaultExecutor, AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) {
super(defaultExecutor, exceptionHandler);
}
//符合切入点的代理对象方法,切入点由buildPointcut()方法返回
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
//原始定义方法
final Method userDeclaredMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
//决定使用哪个AsyncTaskExecutor
AsyncTaskExecutor executor = determineAsyncExecutor(userDeclaredMethod);
if (executor == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No executor specified and no default executor set on AsyncExecutionInterceptor either");
}
//将方法执行包装进Callable中,这样就可以使用线程池进行submit达到多线程异步执行的效果
Callable<Object> task = () -> {
try {
Object result = invocation.proceed();
if (result instanceof Future) {
return ((Future<?>) result).get();
}
}
catch (ExecutionException ex) {
handleError(ex.getCause(), userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleError(ex, userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments());
}
return null;
};
//父类AsyncExecutionAspectSupport方法,使用executor调度执行
return doSubmit(task, executor, invocation.getMethod().getReturnType());
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected String getExecutorQualifier(Method method) {
return null;
}
//重写父类AsyncExecutionAspectSupport
@Override
@Nullable
protected Executor getDefaultExecutor(@Nullable BeanFactory beanFactory) {
Executor defaultExecutor = super.getDefaultExecutor(beanFactory);
return (defaultExecutor != null ? defaultExecutor : new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor());
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
}
//determineAsyncExecutor()方法定义在父类AsyncExecutionAspectSupport中。
protected AsyncTaskExecutor determineAsyncExecutor(Method method) {
AsyncTaskExecutor executor = this.executors.get(method);
if (executor == null) {
Executor targetExecutor;
//如果取得方法或类上的@Async的value属性,然后从容器中找到同名的Executor类型的bean
String qualifier = getExecutorQualifier(method);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(qualifier)) {
targetExecutor = findQualifiedExecutor(this.beanFactory, qualifier);
}
//如果没有qualifier 使用默认的
else {
targetExecutor = this.defaultExecutor.get();
}
if (targetExecutor == null) {
return null;
}
//容器中的Executor可能不是TaskExecutor需要使用TaskExecutorAdapter包装一下
executor = (targetExecutor instanceof AsyncListenableTaskExecutor ?
(AsyncListenableTaskExecutor) targetExecutor : new TaskExecutorAdapter(targetExecutor));
this.executors.put(method, executor);
}
return executor;
}
doSubmit()方法根据目标方法的返回值类型决定他实际的类型,如果目标方法返回值类型不是Future的则返回null。
@Nullable
protected Object doSubmit(Callable<Object> task, AsyncTaskExecutor executor, Class<?> returnType) {
if (CompletableFuture.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
return task.call();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new CompletionException(ex);
}
}, executor);
}
else if (ListenableFuture.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
return ((AsyncListenableTaskExecutor) executor).submitListenable(task);
}
else if (Future.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {
return executor.submit(task);
}
else {
executor.submit(task);
return null;
}
}
以上就是通知的具体逻辑,下面再看切入点的具体实现。
protected Pointcut buildPointcut(Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes) {
ComposablePointcut result = null;
for (Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType : asyncAnnotationTypes) {
//类或方法级别上有@Async注解就可以应用通知
Pointcut cpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(asyncAnnotationType, true);
Pointcut mpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(null, asyncAnnotationType, true);
if (result == null) {
result = new ComposablePointcut(cpc);
}
else {
result.union(cpc);
}
result = result.union(mpc);
}
return (result != null ? result : Pointcut.TRUE);
}
buildPointcut()方法会结合类和方法上的asyncAnnotationType,当然默认是@Async和@Asynchronous,类和方法上一处出现异步注解就会应用通知。
public class AnnotationMatchingPointcut implements Pointcut {
private final ClassFilter classFilter;
private final MethodMatcher methodMatcher;
public AnnotationMatchingPointcut(Class<? extends Annotation> classAnnotationType, boolean checkInherited) {
this.classFilter = new AnnotationClassFilter(classAnnotationType, checkInherited);
this.methodMatcher = MethodMatcher.TRUE;
}
public AnnotationMatchingPointcut(@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> classAnnotationType,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> methodAnnotationType) {
this(classAnnotationType, methodAnnotationType, false);
}
public AnnotationMatchingPointcut(@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> classAnnotationType,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> methodAnnotationType, boolean checkInherited) {
Assert.isTrue((classAnnotationType != null || methodAnnotationType != null),
"Either Class annotation type or Method annotation type needs to be specified (or both)");
if (classAnnotationType != null) {
//类上有@Async返回ture,支持继承的@Async
this.classFilter = new AnnotationClassFilter(classAnnotationType, checkInherited);
}
else {
this.classFilter = ClassFilter.TRUE;
}
if (methodAnnotationType != null) {
//方法级别有@Async返回true
this.methodMatcher = new AnnotationMethodMatcher(methodAnnotationType, checkInherited);
}
else {
this.methodMatcher = MethodMatcher.TRUE;
}
}
@Override
public ClassFilter getClassFilter() {
return this.classFilter;
}
@Override
public MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher() {
return this.methodMatcher;
}
}
3、代理对象的生成
有了通知器接下来看看如果生成代理对象的。
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (this.advisor == null || bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
//如果bean已经到Spring AOP代理对象,则直接将此通知器添加到拦截器链
if (bean instanceof Advised) {
Advised advised = (Advised) bean;
if (!advised.isFrozen() && isEligible(AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean))) {
// Add our local Advisor to the existing proxy's Advisor chain...
if (this.beforeExistingAdvisors) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, this.advisor);
}
else {
advised.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
}
return bean;
}
}
//符合被代理的条件
if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) {
//使用子类的方法创建一个代理工厂
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(bean.getClass(), proxyFactory);
}
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisor);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
// No proxy needed.
return bean;
}
上面逻辑很清晰,如果bean不是Spring AOP代理对象,就使用子类方法isEligible判断是否能做代理对象,如果能则使用子类方法prepareProxyFactory()创建一个ProxyFactory用来生成代理对象,ProxyFactory原理参考/zhuanlan/j2ee/spring/7/22.html。
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor#isEligible()
@Override
protected boolean isEligible(Object bean, String beanName) {
return (!AutoProxyUtils.isOriginalInstance(beanName, bean.getClass()) &&
super.isEligible(bean, beanName));
}
org.springframework.aop.framework.AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor#isEligible(java.lang.Object, java.lang.String)
protected boolean isEligible(Object bean, String beanName) {
return isEligible(bean.getClass());
}
protected boolean isEligible(Class<?> targetClass) {
Boolean eligible = this.eligibleBeans.get(targetClass);
if (eligible != null) {
return eligible;
}
if (this.advisor == null) {
return false;
}
//切入点决定
eligible = AopUtils.canApply(this.advisor, targetClass);
this.eligibleBeans.put(targetClass, eligible);
return eligible;
}
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor#prepareProxyFactory()
@Override
protected ProxyFactory prepareProxyFactory(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass(this.beanFactory, beanName, bean.getClass());
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = super.prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass() && this.beanFactory != null &&
AutoProxyUtils.shouldProxyTargetClass(this.beanFactory, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
return proxyFactory;
}
org.springframework.aop.framework.AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor#prepareProxyFactory()
protected ProxyFactory prepareProxyFactory(Object bean, String beanName) {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
proxyFactory.setTarget(bean);
return proxyFactory;
}