08、 Golang 设计模式:08_组合模式
1、介绍
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构,使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。组合模式依据树形结构来组合对象,用来表示部分以及整体层次。
组合模式(Composite)经常用于树形结构,为了简化代码,使用Composite可以把一个叶子节点与一个父节点统一起来处理。
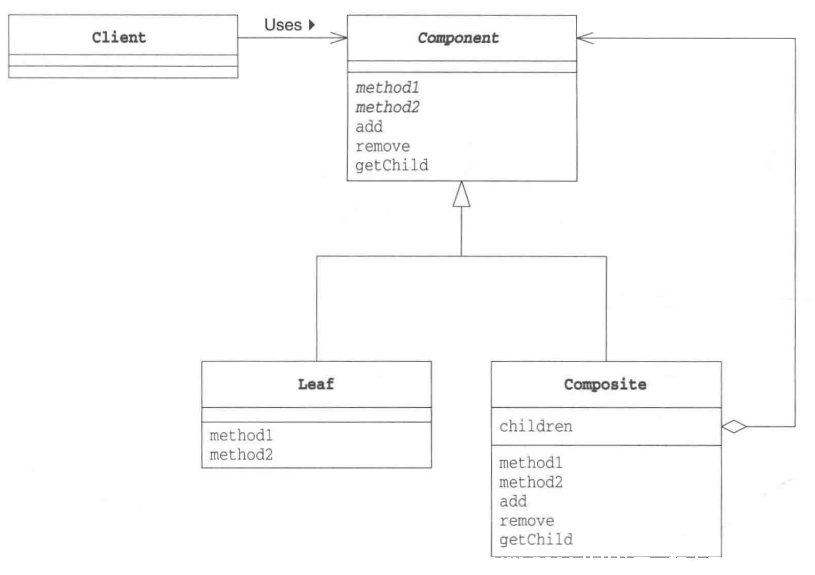
Leaf(树叶):表示“内容”的角色;Composite(复合物):表示容器的角色;Composite:使Leaf角色和Composite角色具有一致性的角色。
2、示例
示例代码:
package main
import "fmt"
type Component interface {
Parent() Component
SetParent(Component)
Name() string
SetName(string)
AddChild(Component)
Print(string)
}
const (
LeafNode = iota
CompositeNode
)
func NewComponent(kind int, name string) Component {
var c Component
switch kind {
case LeafNode:
c = NewLeaf()
case CompositeNode:
c = NewComposite()
}
c.SetName(name)
return c
}
type component struct {
parent Component
name string
}
func (c *component) Parent() Component {
return c.parent
}
func (c *component) SetParent(parent Component) {
c.parent = parent
}
func (c *component) Name() string {
return c.name
}
func (c *component) SetName(name string) {
c.name = name
}
func (c *component) AddChild(Component) {}
func (c *component) Print(string) {}
type Leaf struct {
component
}
func NewLeaf() *Leaf {
return &Leaf{}
}
func (c *Leaf) Print(pre string) {
fmt.Printf("%s-%s\n", pre, c.Name())
}
type Composite struct {
component
childs []Component
}
func NewComposite() *Composite {
return &Composite{
childs: make([]Component, 0),
}
}
func (c *Composite) AddChild(child Component) {
child.SetParent(c)
c.childs = append(c.childs, child)
}
func (c *Composite) Print(pre string) {
fmt.Printf("%s+%s\n", pre, c.Name())
pre += " "
for _, comp := range c.childs {
comp.Print(pre)
}
}
func main() {
root := NewComponent(CompositeNode, "中国")
c1 := NewComponent(CompositeNode, "北京")
c2 := NewComponent(CompositeNode, "上海")
c3 := NewComponent(CompositeNode, "重庆")
l1 := NewComponent(LeafNode, "海淀区")
l2 := NewComponent(LeafNode, "黄浦区")
l3 := NewComponent(LeafNode, "渝北区")
root.AddChild(c1)
root.AddChild(c2)
root.AddChild(c3)
c1.AddChild(l1)
c2.AddChild(l2)
c3.AddChild(l3)
root.Print("")
}
UML:
