03、数据结构与算法 - 基础:栈
1. 栈的定义
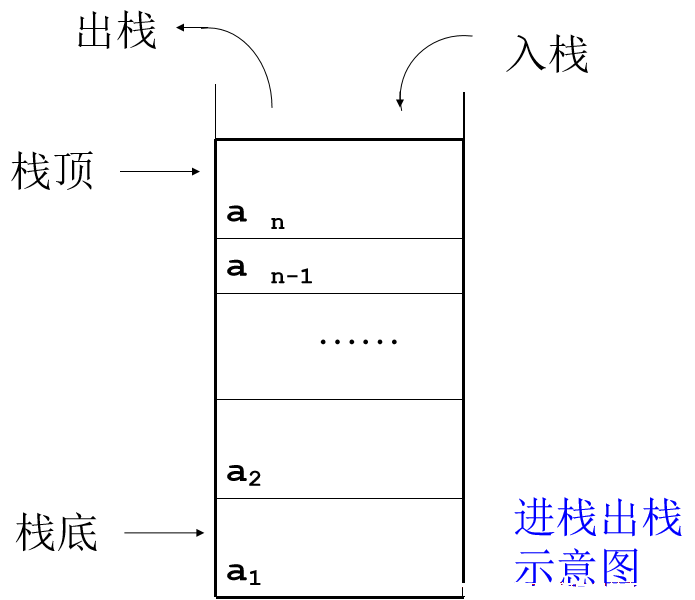
- 栈,也叫堆栈,是最常用也是最重要的数据结构之一。
- 栈(Stack)是限定仅在表的一端进行插入或删除操作的线性表,通常称插入、删除的这一端为栈顶(Top),另一端为栈底(Bottom)。当表中没有元素时称为空栈。
- 栈操作的特点:后进先出,先进后出。
- 因此,栈称为后进先出表(LIFO, Last In First Out)。
示意图:
2. 栈的基本运算
- 初始化栈InitStack(*S)
- 压栈Push(*S,x) ——在栈顶插入元素
- 出栈Pop(*S,x) ——在栈顶删除元素
- 取栈顶元素GetTop(S,x)
- 判栈空Empty(S)
栈的几种状态(最大长度MaxSize为4):栈空、压栈、栈满、出栈
3. 栈的存储结构
栈有两种表示方法:顺序存储和链式存储
3.1 顺序栈
采用顺序存储结构的栈简称为顺序栈。是利用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素,同时附设整型变量top指示栈顶元素在顺序栈中的位置。
// 顺序栈数据类型的C语言描述如下:
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct {
DataType data[MaxSize];
int top;
}Stack;
// top:栈顶指针。取值范围为0~MaxSize-1。
// top==-1表示栈空,top==MaxSize-1表示栈满。
// 初始化栈InitStack(S)
int InitStack(Stack *S)
{
S->top=-1;
return 1;
}
// 压栈Push(S,x)
int Push(Stack *S,DataType x)
{
if(S->top==MaxSize-1)
{
printf("\n Stack is full!");
return 0;
}
S->top++;
S->data[S->top]=x;
return 1;
}
// 判栈空EmptyStack(S)
int EmptyStack(Stack *S)
{
return (S->top==-1?1:0);
}
// 出栈Pop(S,x)
int Pop(Stack *S,DataType *x)
{
if(EmptyStack(S))
{
printf("\n Stack is free!");
return 0;
}
*x=S->data[S->top];//记住要删除的元素值
S->top--;
return 1;
}
// 取栈顶元素GetTopStack(S)
DataType GetTop(STACK *S)
{
DataType x;
if(EmptyStack(S))
{
printf("\n Stack is free!");
exit(1);
}
x=S->data[S->top];
return x;
}
View Code
3.1 链栈:栈的链式存储结构
链栈结构示意图:
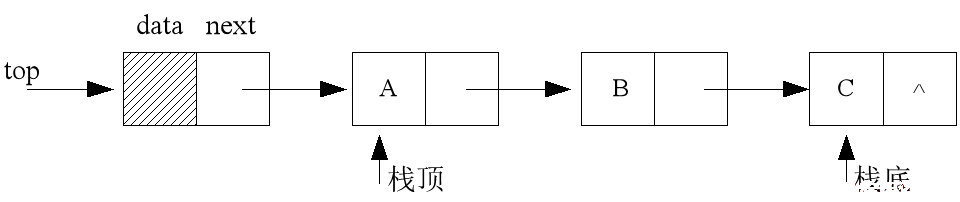
top栈顶指针,惟一的确定一个链栈。 链栈通常带有一个表头结点,所以top->next才指示栈顶元素。
// 链栈的C语言描述如下:
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data;
struct node *next;
}Stack;
Stack * InitStack()
{
Stack *top;
top=(Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
top->next=NULL;
return top;
}
//进栈
int Push(Stack *top,Pos x)
{
Stack *s;
s=(Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
if(!s) //当s==NULL return 0
return 0;
s->data=x;
s->next=top->next; //新申请空间的指针域保存上一个结点的地址
top->next=s; //头指针域保存新结点地址
return 1;
}
//判断栈空
int EmptyStack(Stack *top)
{
if(top->next==NULL)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
//出栈
int Pop(Stack *top,Pos *e)
{
Stack *s;
if(EmptyStack(top))
return 0;
s=top->next; //取第一个结点的地址
*e=s->data; //返第一结点数据
top->next=s->next; //头结点指针域存第二结点地址
free(s);
return 1;
}
//取栈顶元素
int GetTopStack(Stack *top,Pos *e)
{
Stack *s;
if(EmptyStack(top))
return 0;
s=top->next;
*e=s->data;
return 1;
}
View Code